Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A group of inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract consisting of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Cronh’s Disease:
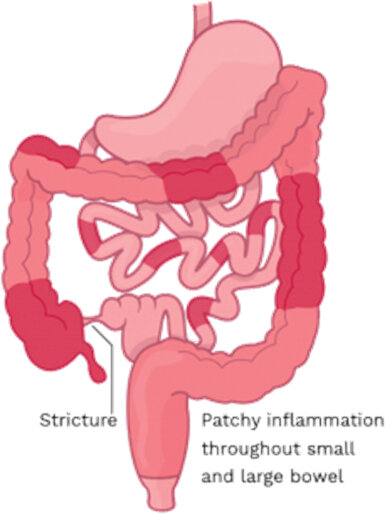
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract.
Can affect any part of the GI tract, but most commonly the end of the small bowel (ileum) and the beginning of the colon
Can affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall
Inflammation can “skip,” leaving normal areas in between patches of diseased intestine
Modified from https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-crohns-disease/overview
Ulcerative Colitis:
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colon, affecting the lining of the colon and causes small sores, or ulcers, to form. Those ulcers produce pus and mucous, which cause abdominal pain and the need to frequently empty your colon.
Only the colon, also called the large intestine, is affected
Affects only the innermost lining of the colon
Inflammation of the intestine does not “skip”
Modified from https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-ulcerative-colitis/overview
The biology behind IBD:
Current treatments for IBD:
First line therapy for mild and moderate cases are aminosalicylates, corticosteroids and small molecule immunomodulators (e.g., methotrexate)
Biologics are usually used to treat moderate and severe cases or are used as combination therapy in order to maintain disease remission
ALL the current therapies are generally immune suppressive
Crohn’s disease:
Around 70% of Crohn’s patients eventually require surgery
Surgical recurrence rate: ~30% at 3 years, ~60% at 10 years
Ulcerative Colitis:
Over 25-33% of UC patients eventually require surgery
Depending on the severity of the disease, surgery may involve only the colon or the entire large intestine
Back to PTM-001